Most equations need to be solved numerically since no close-form expression representing their solutions can be obtained. For polynomial equations of order 1, 2, 3, 4 exact solutions can be obtained. I have created a series of solvers up to a cubic solver, that can be used to obtain most exact solutions. Of course with floating point errors, not everything is going to come out looking clean. To be able to handle complex numbers I made a simplified version of a complex number without all the mathematical operations.
If you call the cubicSolve function with a = 0 then the solver falls back on the quadratic solver, the quadratic solver will fallback on the linear solver and linear solver will return an empty array.
Example Usage
let solutions = cubicSolve(a: 1, b: 1, c: 1, d: 1)
let realSolutions = solutions.filter({ $0.isReal }) // filters for only real values
let complexSolutions = solutions.filter({ !$0.isReal }) // filters for only complex values
Complex Number
Here I made a struct to house the real and imaginary portions of a complex number, I added an isReal property that returns a Bool depending on whether the imaginary portion is 0 or not. Lastly I added two convieniences, a static zero function and conformance to CustomStringConvertible. CustomStringConvertible, gives us an easy way to view our complex number.
struct ComplexNumber {
var real: Double
var imaginary: Double
public init(_ real: Double, _ imaginary: Double) {
self.real = real
self.imaginary = imaginary
}
public init(_ real: Double) {
self.real = real
self.imaginary = 0
}
var isReal: Bool { imaginary == 0 }
}
extension ComplexNumber {
static func zero() -> Self {
return ComplexNumber(0, 0)
}
}
extension ComplexNumber: CustomStringConvertible {
var description: String {
return "(Real: \(real), Imaginary: \(imaginary))"
}
}
Linear Solver
I will give you a hint for this one, subtract from both sides first. But for real the answer is literally just $\frac{-b}{a}$, oh yeah and $a$ can’t be 0
func linearSolve(a: Double, b: Double) -> [ComplexNumber] {
if a == 0 { return [] }
return [ComplexNumber(-b/a)]
}
Quadratic Solver
The next solver is actually a little challenging to implement. The reason is that since Doubles are floating point numbers, machine precision plays a factor in the exactness of our answer. To handle the rounding errors we define a value to be the threshold. This allows us to get much cleaner answers for certain quadratics. Just because I had one lying around heres the actual proof of the quadratic formula, I know you haven’t seen it in a long time.
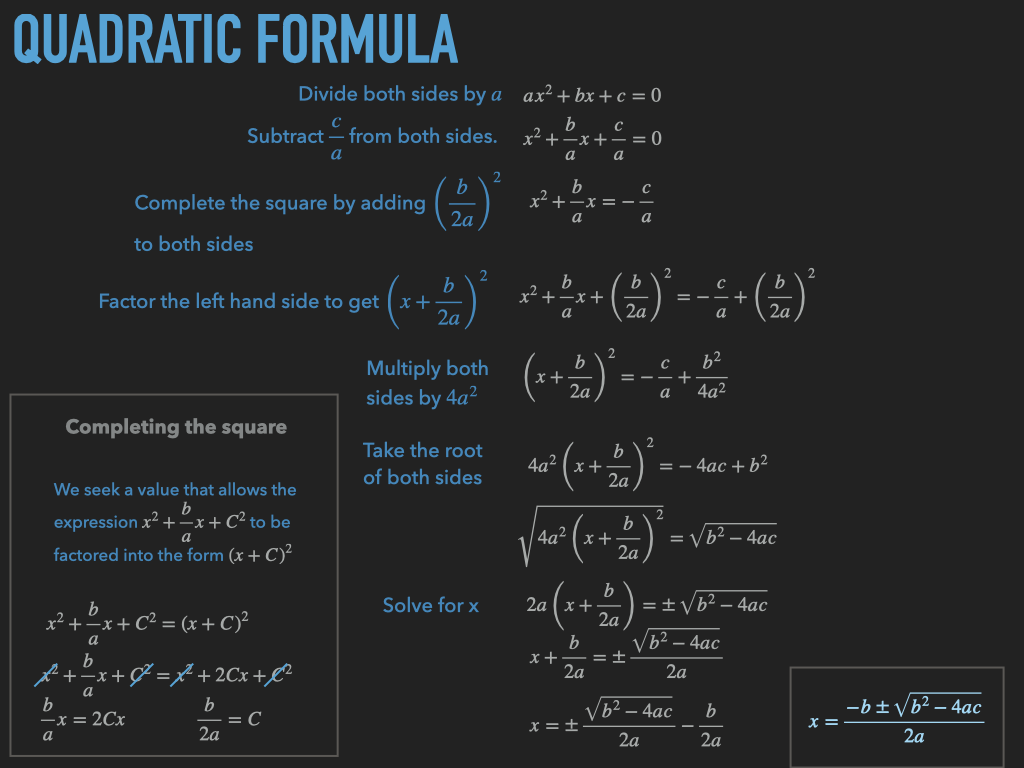
Now for the procedure
- calculate discriminant $d = b^2 -4ac$.
- if $d > 0$ , equation has two distinct real roots exist.
- if $d = 0$, equation has two repeated real roots.
- if $d < 0$ equation has two complex roots.
func quadraticSolve(a: Double, b: Double, c: Double, threshold: Double = 0.0001) -> [ComplexNumber] {
if a == 0 { return linearSolve(a: b, b: c) }
var roots = [ComplexNumber]()
var d = pow(b, 2) - 4*a*c // discriminant
// Check if discriminate is within the 0 threshold
if -threshold < d && d < threshold { d = 0 }
if d > 0 {
let x_1 = ComplexNumber((-b + sqrt(d))/(2*a))
let x_2 = ComplexNumber((-b - sqrt(d))/(2*a))
roots = [x_1, x_2]
} else if d == 0 {
let x = ComplexNumber(-b/(2*a))
roots = [x, x]
} else if d < 0 {
let x_1 = ComplexNumber(-b/(2*a), sqrt(-d)/(2*a))
let x_2 = ComplexNumber(-b/(2*a), -sqrt(-d)/(2*a))
roots = [x_1, x_2]
}
return roots
}
Cubic Solver
Now for the moneyshot, the cubic solver. This one is a real procedure. So next time you see Cardano say thank you. So here it is
important: $a, b, c, d$ should all be real numbers.
Procedure
- Divide both sides of equation by a.
- In the case that $a = 0$ fallback onto the
quadraticSolve. - other wise move on to step 2. The equation should now look as follows $x^3 + \frac{b}{a}x^2 + \frac{c}{a}x + \frac{d}{a} = 0$.
- In the case that $a = 0$ fallback onto the
- Calculate the discriminant D
When $D > 0$ , one real root with 2 complex conjugate roots.
When $D = 0$ , all roots are real and atleast 2 are repeated.
When $D < 0$, all roots are real and unequal.
-
If $D > 0$,
$x_1 = s + t - \frac{a_1}{3}$: The only real solution
$x_2 = -\frac{s+t}{2} - \frac{a_1}{3} + \frac{\sqrt{3}(s - t)}{2}i$: First complex solution
$x_3 = -\frac{s+t}{2} - \frac{a_1}{3} - \frac{\sqrt{3}(s - t)}{2}i$: Second complex solution
-
Else if $D = 0$ or $D < 0$ Trigonometry can be used Let $\theta = \arccos{\frac{r}{\sqrt{-q^3}}}$
$x_1 = 2\sqrt{-q}\cos{\left(\frac{\theta}{3}\right)} - \frac{a_1}{3}$
$x_2 = 2\sqrt{-q}\cos{\left(\frac{\theta}{3} + \frac{2\pi}{3}\right)} - \frac{a_1}{3}$
$x_3 = 2\sqrt{-q}\cos{\left(\frac{\theta}{3} + \frac{4\pi}{3}\right)} - \frac{a_1}{3}$
func cubicSolve(a: Double, b: Double, c: Double, d: Double, threshold: Double = 0.0001) -> [ComplexNumber] {
// if not a cubic fall back to quadratic
if a == 0 { return quadraticSolve(a: b, b: c, c: d) }
var roots = [ComplexNumber]()
let a_1 = b/a
let a_2 = c/a
let a_3 = d/a
let q = (3*a_2 - pow(a_1, 2))/9
let r = (9*a_1*a_2 - 27*a_3 - 2*pow(a_1, 3))/54
let s = cbrt(r + sqrt(pow(q, 3)+pow(r, 2)))
let t = cbrt(r - sqrt(pow(q, 3)+pow(r, 2)))
var d = pow(q, 3) + pow(r, 2) // discriminant
// Check if d is within the zero threshold
if -threshold < d && d < threshold { d = 0 }
if d > 0 {
let x_1 = ComplexNumber(s + t - (1/3)*a_1)
let x_2 = ComplexNumber(-(1/2)*(s+t) - (1/3)*a_1, (1/2)*sqrt(3)*(s - t))
let x_3 = ComplexNumber(-(1/2)*(s+t) - (1/3)*a_1, -(1/2)*sqrt(3)*(s - t))
roots = [x_1, x_2, x_3]
} else if d <= 0 {
let theta = acos(r/sqrt(-pow(q, 3)))
let x_1 = ComplexNumber(2*sqrt(-q)*cos((1/3)*theta) - (1/3)*a_1)
let x_2 = ComplexNumber(2*sqrt(-q)*cos((1/3)*theta + 2*Double.pi/3) - (1/3)*a_1)
let x_3 = ComplexNumber(2*sqrt(-q)*cos((1/3)*theta + 4*Double.pi/3) - (1/3)*a_1)
roots = [x_1, x_2, x_3]
}
return roots
}
Things To Remember
The threshold value is used to clamp the discriminant to 0 so that the cubic and quadratic solvers will follow the correct path, without it real solutions end up having a non zero imaginary part.
These solvers aren’t perfect and Im sure someone can find more features or optimizations. I just wanted to make a good base to work from that is not to complicated to deconstruct or understand.
- references: Cubic Equation
